Vingroup AI Engineer Program - Computer Vision Project
Project Title
Image Classification of Stroke Blood Clot Origin
Introduction
The primary objective of this project is to classify the origin of blood clots in ischemic stroke using whole slide digital pathology images. Specifically, the model aims to distinguish between two major acute ischemic stroke (AIS) etiology subtypes:
- Cardiac origin
- Large artery atherosclerosis origin
Accurate classification of blood clot origins significantly aids healthcare providers in prescribing precise post-stroke therapeutic management, thus reducing the risk of recurrent strokes.
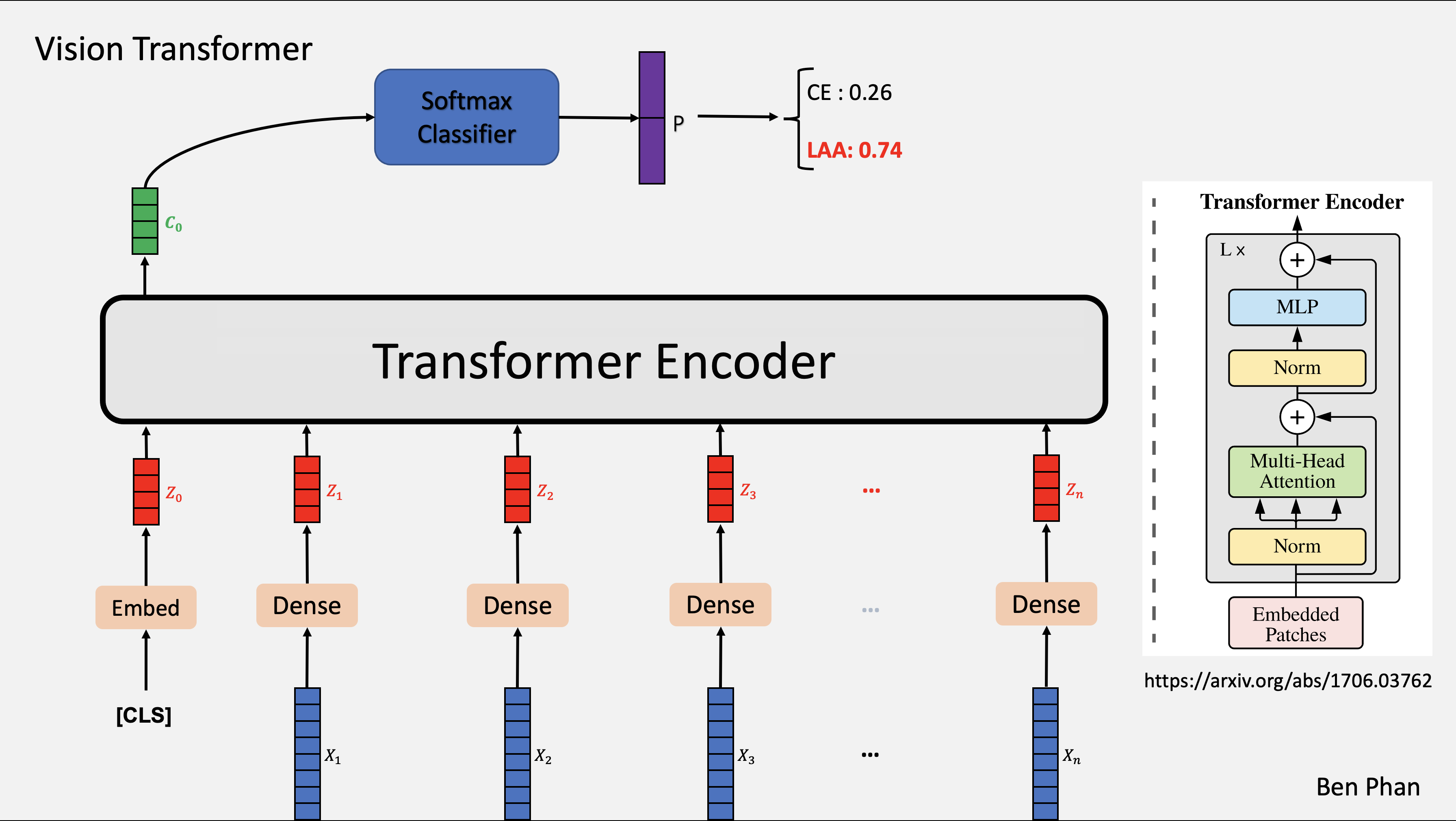
Vision Transformer (ViT) Model Overview
Vision Transformer (ViT) is a deep learning architecture inspired by the original Transformer model proposed by Vaswani et al. (2017). ViT applies self-attention mechanisms to image processing tasks without relying on convolutional layers traditionally used in CNNs.
ViT Architecture and Pipeline
The Vision Transformer model follows these primary steps:
1. Splitting Images into Patches
Given an input image $x$ with dimensions $H \times W \times C$:
\[x \in \mathbb{R}^{H \times W \times C}\]The image is divided into $N$ non-overlapping patches, each of size $P \times P$:
\[N = \frac{H W}{P^2}, \quad x_p^i \in \mathbb{R}^{P^2 \cdot C}, \quad i = 1, 2, ..., N\]2. Linear Embedding
Each patch is flattened and linearly projected to a $D$ dimensional embedding space:
\[z_i = E x_p^i + E_{pos}, \quad i = 1, 2, ..., N\]Where:
- $E$ is the embedding matrix.
- $E_{pos}$ represents positional embeddings.
3. Transformer Encoder
The embedded patches are concatenated with a learnable classification token $x_{class}$:
\[z_0 = [x_{class}; z_1; z_2; ...; z_N]\]Each Transformer encoder block consists of:
- Layer Normalization (LN)
- Multi-head Self-Attention (MSA)
Self-attention mechanism is defined as:
\[\text{Attention}(Q,K,V) = \text{softmax}\left(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}}\right)V\]Multi-head attention combines multiple attention heads:
\[\text{MultiHead}(Q,K,V) = [\text{head}_1; ...; \text{head}_h]W^O\]Each head computes attention separately :
\[\text{head}_i = \text{Attention}(QW_i^Q, KW_i^K, VW_i^V)\]4. Feed-Forward Network (MLP)
Each encoder block includes an MLP with GELU activation function:
\[\text{MLP}(x) = \text{GELU}(xW_1 + b_1)W_2 + b_2\]5. Classification Head
After passing through transformer encoder blocks, the final classification token embedding $z_L^0$ is fed into an MLP head for classification:
\[y = \text{softmax}(\text{MLP}(z_L^0))\]Training Strategy
The ViT model undergoes two training phases:
- Pre-training on large-scale datasets (e.g., ImageNet).
- Fine-tuning on stroke blood clot classification data.
Advantages and Limitations
| Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Effectively captures global context | Requires large datasets |
| Less inductive bias than CNNs | Computationally expensive |
| Highly parallelizable | Sensitive to hyperparameters |
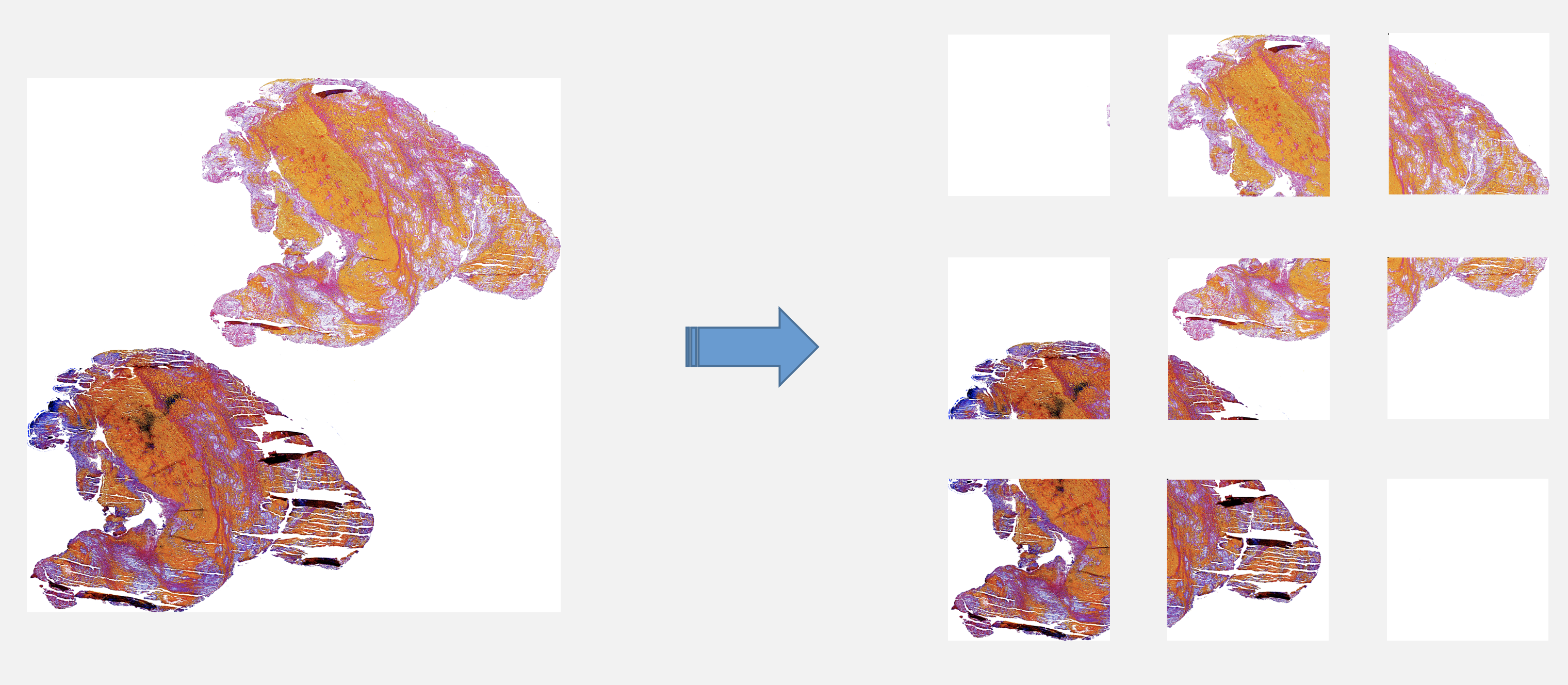
Model Pipeline
Video Demonstration
Authors and Contributors
| Name | University | Contact |
|---|---|---|
| Phan Ben | Danang University of Technology | phanben110@gmail.com |
| Lương Trọng Trí | Hanoi University of Technology | |
| Nguyễn Thị Thắm | Hanoi University of Technology | |
| Trần Thị Hoài Thương | Danang University of Technology |
Acknowledgments
- Kaggle Competition
- NCBI Research
- PathML Documentation
- Macenko Stain Normalization
- Quantifying the effects of data augmentation and stain color normalization in computational pathology.
- Tailoring automated data augmentation to H&E-stained histopathology.